Poly(triphenyl ethene) and poly(tetraphenyl ethene): synthesis, aggregation-induced emission property and application as paper sensors for effective nitro-compounds detection†
Abstract
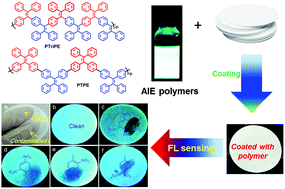
Two unique aggregation-induced emission (AIE) active polymers poly(triphenyl ethene) (PTriPE) and poly(tetraphenyl ethene) (PTPE), comprising sole repeating units, triphenyl and tetraphenyl, respectively, were synthesized through the Suzuki coupling of (2,2-dibromoethene-1,1-diyl)dibenzene and related di-boronic acid or ester compounds. The polymers PTriPE and PTPE had number-molecular weights (10 100–17 400) with polydispersity indices of 1.5–1.7, and they were soluble in common organic solvents. The polymers in THF/H2O mixtures were able to form remarkably stable nanoparticles and no agglomeration was observed even when stored at 4 °C for several months. The polymer PTriPE and PTPE exhibited much more significant AIE activities when compared to their corresponding small AIE molecule 1,1,2,2-tetraphenylethene (TPE) and 4,4′-(2,2-diphenylethene-1,1-diyl)dibiphenyl (DPDB) in THF–H2O mixtures. The fluorescence of polymer nanoparticles in THF/H2O mixture could be quenched by various nitro-compounds, and PTriPE nanoparticles demonstrated a better fluorescence quenching response than PTPE. The film formed by PTriPE nanoparticles showed a reasonable fluorescence quenching response to nitro-compounds, for example, ∼5 ppb in the case of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene vapor, despite its thickness approaching the micrometer level. Furthermore, PTriPE-based paper sensors were fabricated from its polymer nanoparticles’ solution, and is still effective with a polymer surface concentration as low as 1.0 μg cm−2 in detecting various nitro-compounds at a scale less than 1 ng, making it a useful tool for a quick, inexpensive and most importantly, highly sensitive detection of nitro-compounds based explosives.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...