Synthesis of poly(allyl 2-ylidene-acetate) and subsequent post-polymerization modification via thiol–ene reaction†
Abstract
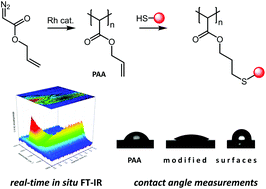
Poly(allyl 2-ylidene-acetate) (Mw = 125 300 g mol−1) was synthesized via rhodium mediated catalysis of allyl 2-diazoacetate and its polymerization kinetics and polymer characteristics are presented and discussed. This polymer represents the first functional polymethylene accessible by a thiol–ene click-chemistry post-polymerization modification. Thiol–ene reactions were conducted under UV-irradiation utilizing 2,2-dimethoxy-2-phenylacetophenone as a photo-initiator. Differences to other polymethylenes, such as the inherent ability of poly(allyl 2-ylidene-acetate) to self-crosslink, and polymer characteristics are discussed. The inherent ability to self-crosslink is further utilized to form stable thin films. Subsequent modification of the surface leads to different surface properties as proven by contact angle measurement.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...