Novel associative nanoparticles grafted with hydrophobically modified zwitterionic polymer brushes for the rheological control of aqueous polymer gel fluids
Abstract
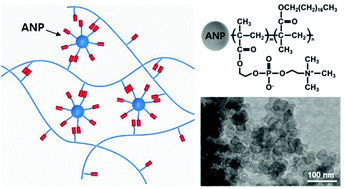
This study reports a robust and straightforward approach to synthesize associative nanoparticles (ANPs) that can modify the rheological properties of aqueous polymer gel fluids. The ANPs were synthesized by grafting hydrophobically modified hygroscopic zwitterionic poly(2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine (MPC)-co-stearyl methacrylate (SMA)) brushes onto 20 nm sized silica NPs via surface-mediated living radical polymerization. SMA having an alkyl chain (C18) was copolymerized with MPC to induce hydrophobic interaction with the corresponding alkyl chain of associative polymers that were freely dissolved in the aqueous phase. The incorporation of the ANPs into the associative polymer solution significantly enhanced the viscosity of the solution by a factor of five. This observation indicates that the ANPs act as nanoscale particulate crosslinkers due to their effective association with the polymers in the solution, leading to the formation of an ANP-mediated polymer gel structure. The ANP-reinforced polymer gel system prepared herein exhibited improved tolerance to pH and salinity, which is attributed to the retarded polymer chain relaxation from the particulate crosslink junction point.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...