An ATRP-based approach towards water-borne anisotropic polymer–Gibbsite nanocomposites†
Abstract
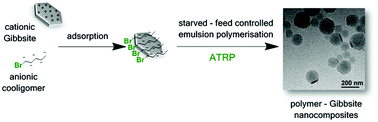
Polymer–Gibbsite composite latex particles were synthesised via an atom transfer radical polymerisation (ATRP) based approach. A random ATRP cooligomer, consisting of acrylic acid and butyl acrylate units, was synthesized using ATRP. This cooligomer was used as a stabiliser for the Gibbsite platelets and served as a macroinitiator for copper-mediated starved-feed emulsion polymerisation. Using a hydrophobic ligand for Cu2+ and optimising the feeding profile of ascorbic acid and the [ascorbic acid]/[Cu2+] ratio, successful Activator ReGenerated by Electron Transfer (ARGET) ATRP emulsion polymerisation was conducted in a controlled way, using only the anionic ATRP cooligomer as a surfactant. Cryo-TEM characterisation revealed a “muffin-like” morphology of the resulting composite latex particles, which was not affected by monomer feed composition and feeding profile.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...