Reduction/pH dual-responsive nano-prodrug micelles for controlled drug delivery†
Abstract
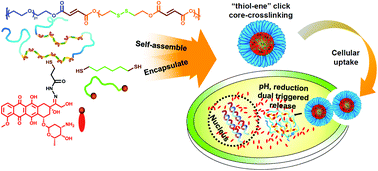
In this work, an amphiphilic alternating multiblock copolymer poly[oligo(ethylene glycol)fumarate-co-dithiodiethanol fumarate] (POEGSSFM) with multiple enes and disulfides in hydrophobic blocks was synthesized facilely by the “one-pot” method, which can self-assemble into nano-scaled micelles and encapsulate mercapto-modified doxorubicin (DOX-SH) with 1,6-hexanedithiol into the core for in situ drug conjugation and core-crosslinking (CCL) via a thiol–ene “click” reaction, resulting in a reduction and pH dual-responsive nano-prodrug micelle (CCL-POEGSSFM-DOX). The obtained nano-prodrug micelles presented stable nano-scaled spherical particles under physiological conditions, while quickly dissociating in response to 10 mM DL-dithiothreitol (DTT). As doxorubicin (DOX) was conjugated via a pH-sensitive hydrazone linkage, the in vitro release results showed a minimized release of DOX at pH 7.4, while a rapid release at pH 5.8. Particularly, the release of DOX in an acidic environment could also be significantly accelerated by treating with DTT, owing to the cleavage of the disulfide bonds, which leads to the disassociation of the micelles. Confocal laser scanning microscopy further demonstrated that the nano-prodrug can be easily taken into cells, presenting a rapid DOX release in the cytoplasm. Cytotoxicity assay indicated that the nano-prodrug micelles exhibited excellent cytotoxic effects on HeLa cells, while blank CCL-POEGSSFM micelles were biocompatible. This facilely prepared pH and reduction dual-responsive CCL nano-prodrug would be a promising candidate for cancer chemotherapy.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...