Azide-based heterobifunctional poly(ethylene oxide)s: NaN3-initiated “living” polymerization of ethylene oxide and chain end functionalizations†
Abstract
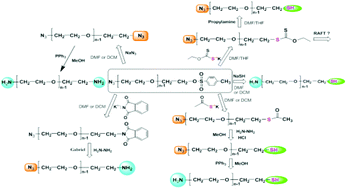
In this study, sodium azide (NaN3) was employed as a functional anionic initiator to polymerize ethylene oxide in N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) leading to the production of the reactive polymeric alkoxide. The molecular weights of all products were controlled within the 2800–10 000 g mol−1 range on the basis of the stoichiometric balance. NaN3-initiated polymerization of ethylene oxide (EO) and chain end functionalization of the resulting alkoxide were found to be a simple and efficient method for synthesizing heterobifunctional PEOs. The reaction route via chain end tosylation of α-azide PEOs was found to yield almost quantitative functionalizations for the synthesis of α-azide-ω-tosyl PEO, α-azide-ω-thiol PEO, and α-amine-ω-thiol PEO (over 98 mol%).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...