Effect of proline on biochemical and molecular mechanisms in lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) exposed to UV-B radiation
Abstract
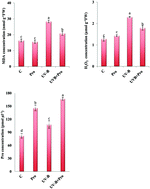
The purpose of the present study was to evaluate the role of proline (Pro) in relieving UV-B radiation-induced oxidative stress in lettuce. Lettuce seedlings were exposed to 3.3 W m−2 UV-B radiation for 12 h after pre-treatment sprayed with 20 mM Pro. The data for malondialdehyde (MDA), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), endogenous Pro level, the activities of antioxidant enzymes [superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), ascorbate peroxidase (APX), and peroxidase (POD)], total phenolic concentration, antioxidant capacity, expression of phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL), γ-tocopherol methyltransferase (γ-TMT) and proline dehydrogenase (ProDH) genes, phytohormone levels such as abscisic acid (ABA), gibberellic acid (GA), indole acetic acid (IAA) and salicylic acid (SA), soluble sugars and organic acids were recorded. It was found that Pro alleviated the oxidative damage in the seedlings of lettuce as demonstrated by lower lipid peroxidation and H2O2 content, increasing the endogenous Pro level, the activity of antioxidant enzymes, total phenolic concentration and the antioxidant capacity. Additionally, it was revealed that exogenous application of Pro enhanced the levels of GA, IAA, the concentrations of soluble sugars and organic acids and expressions of PAL, γ-TMT and ProDH genes as compared to the control. The results obtained in this study suggest that pre-treatment with exogenous Pro provides important contributions to the increase in the UV-B tolerance of lettuce by regulating the biochemical mechanisms of UV-B response.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...