Cyclodextrin-based facial amphiphiles: assessing the impact of the hydrophilic–lipophilic balance in the self-assembly, DNA complexation and gene delivery capabilities†
Abstract
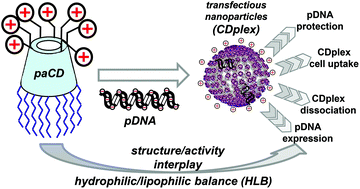
Exhaustive structure–efficacy relationship studies on nonviral gene delivery systems are often hampered by the ill-defined or polydisperse nature of the formulations. Facial amphiphiles based on rigid cage-type molecular scaffolds offer unique possibilities towards these studies. Taking advantage of regioselective functionalization schemes, we have synthesized a library of cationic cyclodextrin (CD) derivatives combining a range of hydrophilic and lipophilic domains. We have scrutinized how the hydrophilic–lipophilic balance (HLB) around the CD scaffold determines their self-assembly capabilities and the DNA binding and release abilities of the corresponding CD : DNA nanocomplexes (CDplexes). These features have been ultimately correlated with their capabilities to deliver a reporter luciferase-encoding pDNA into COS-7 cells. The ensemble of results demonstrates that fine tuning of the HLB is critical to induce compaction of DNA by the CD-based facial amphiphiles into transfection-productive CDplexes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...