Synthesis and biological evaluation of N-naphthoyl-phenylglyoxamide-based small molecular antimicrobial peptide mimics as novel antimicrobial agents and biofilm inhibitors†
Abstract
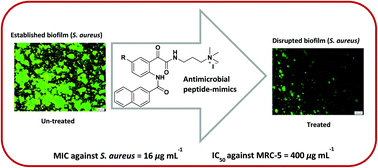
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are a key component of the human immune system. Synthetic AMP mimics represent a novel strategy to counteract the increasing incidence of antimicrobial resistance. Here, we describe the synthesis of novel glyoxamide derivatives via ring-opening reactions of N-hexanoyl, N-benzoyl and N-naphthoylisatins with N,N-dimethylethane-1,2-diamine and N,N-dimethylpropane-1,3-diamine. These were converted to both the hydrochloric acid (HCl) or quaternary ammonium iodide (MeI) salts and their antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus was investigated by their zone-of-inhibition and minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC). The HCl salt 22b exhibited the lowest MIC of 16 μg mL−1, whereas the corresponding MeI salt 22c had a MIC of 39 μg mL−1. We also investigated the in vitro toxicity of active compounds against the MRC-5 normal human lung fibroblasts and their activity against established biofilm in S. aureus.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...