Structure–activity & structure–toxicity relationship study of salinomycin diastereoisomers and their benzoylated derivatives†
Abstract
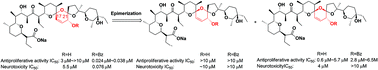
Salinomycin diastereoisomers and their benzoylated derivatives were synthesized and evaluated for both antiproliferative activity and neurotoxicity in vitro. The results indicated that the stereoscopic configurations of the spiro C17 and C21 atoms as well as the benzoyl groups of O-20 on the rigid B/C/D spiro-ketal structures are crucial for biological activity and neural toxicity. In general, there are some positive correlations between the antiproliferative activity and neurotoxicity in these salinomycin derivatives, indicating possibly similar mechanisms of action.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...