Synthesis of characteristic Mycobacterium peptidoglycan (PGN) fragments utilizing with chemoenzymatic preparation of meso-diaminopimelic acid (DAP), and their modulation of innate immune responses†
Abstract
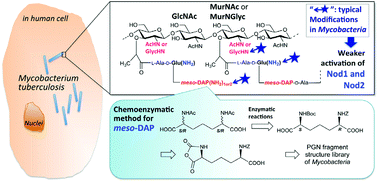
Peptidoglycan (PGN) is a major component of bacterial cell wall and is recognized as a potent immunostimulant. The PGN in the cell envelope of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis has been shown to possess several unique characteristics including the presence of N-glycolyl groups (in addition to N-acetyl groups) in the muramic acid residues, and amidation of the free carboxylic acid of D-Glu or of meso-DAP in the peptide chains. Using a newly developed, highly stereoselective, chemoenzymatic approach for the synthesis of meso-DAP in peptide stems, we successfully synthesized for the first time, a series of Mycobacterium PGN fragments that include both mono- and disaccharides of MurNGlyc or 1,6-anhydro-MurNGlyc, as well as peptide-amidated variants. The ability of these PGN fragments to stimulate the immune system through activation of human Nod1 and Nod2 was examined. The PGN fragments were found to modulate immune stimulation, specifically, amidation at the D-Glu and meso-DAP in the peptide stem strongly reduced hNod1 activation. This effect was dependent on modification position. Additionally, N-glycolyl (instead of acetyl) of muramic acid was associated with slightly reduced human Nod1 and Nod2 stimulatory capabilities.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...