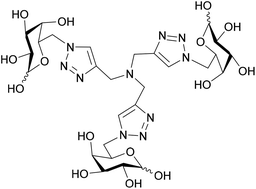
Synthesis of the copper chelator TGTA and evaluation of its ability to protect biomolecules from copper induced degradation during copper catalyzed azide–alkyne bioconjugation reactions†
Abstract
One of the most successful bioconjugation strategies to date is the copper(I)-catalyzed cycloaddition reaction (CuAAC), however, the typically applied reaction conditions have been found to degrade sensitive biomolecules. Herein, we present a water soluble copper chelator which can be utilized to protect biomolecules from copper induced degradation.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...