Strain-induced effects in the electronic and spin properties of a monolayer of ferromagnetic GdAg2†
Abstract
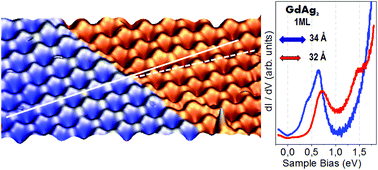
We report on the structural, electronic and magnetic properties of a monolayer of GdAg2, forming a moiré pattern on Ag(111). Combining scanning tunneling microscopy and ab initio spin-polarized calculations, we show that the electronic band structure can be shifted linearly via thermal controlled strain of the intra-layer atomic distance in the range of 1–7%, leading to lateral hetero-structuring. Furthermore, the coupling of the incommensurable GdAg2 alloy layer to the Ag(111) substrate leads to spatially varying atomic relaxation causing subsurface layer buckling, texturing of the electronic and spin properties, and inhomogeneity of the magnetic anisotropy energy across the layer. These results provide perspectives for control of electronic properties and magnetic ordering in atomically-thin layers.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...