In situ electrochemical activation of Ni-based colloids from an NiCl2 electrode and their advanced energy storage performance†
Abstract
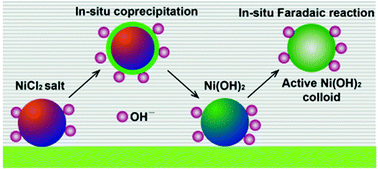
The formation of electrochemical activated cations in electrode materials to induce multiple-electron transfer reactions is a challenge for high-energy storage systems. Herein, highly electroactive Ni-based colloidal electrode materials have been synthesized by in situ electrochemical activation of a NiCl2 electrode. The highest specific capacitance of the activated Ni-based electrodes was 10 286 F g−1 at a current density of 3 A g−1, indicating that a three-electron Faradaic redox reaction (Ni3+ ↔ Ni) occurred. Upon potential cycling and constant potential activation, a decrease in the charge transfer resistance can be found. Activation and utilization of multiple-electron reactions is an efficient route to increase the energy density of supercapacitors. This newly designed colloidal pseudocapacitor is compatible with inorganic pseudocapacitor chemistry, which enables us to use metal cations directly via their commercial salts rather than their oxide/hydroxide compounds.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...