Post passivation light trapping back contacts for silicon heterojunction solar cells†
Abstract
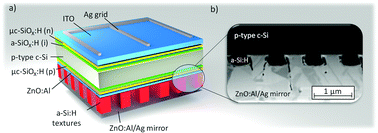
Light trapping in crystalline silicon (c-Si) solar cells is an essential building block for high efficiency solar cells targeting low material consumption and low costs. In this study, we present the successful implementation of highly efficient light-trapping back contacts, subsequent to the passivation of Si heterojunction solar cells. The back contacts are realized by texturing an amorphous silicon layer with a refractive index close to the one of crystalline silicon at the back side of the silicon wafer. As a result, decoupling of optically active and electrically active layers is introduced. In the long run, the presented concept has the potential to improve light trapping in monolithic Si multijunction solar cells as well as solar cell configurations where texturing of the Si absorber surfaces usually results in a deterioration of the electrical properties. As part of this study, different light-trapping textures were applied to prototype silicon heterojunction solar cells. The best path length enhancement factors, at high passivation quality, were obtained with light-trapping textures based on randomly distributed craters. Comparing a planar reference solar cell with an absorber thickness of 280 μm and additional anti-reflection coating, the short-circuit current density (JSC) improves for a similar solar cell with light-trapping back contact. Due to the light trapping back contact, the JSC is enhanced around 1.8 mA cm−2 to 38.5 mA cm−2 due to light trapping in the wavelength range between 1000 nm and 1150 nm.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...