Post-synthetic modification of an amino-functionalized metal–organic framework for highly efficient enrichment of N-linked glycopeptides†
Abstract
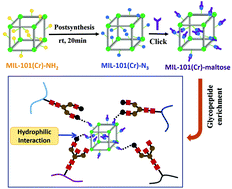
A maltose-functionalized metal–organic framework (MOF), MIL-101(Cr)-maltose, was developed via a simple two step post-synthetic modification of MIL-101(Cr)-NH2. With the use of this nanomaterial, 33 glycopeptides were detected from the digest of human immunoglobulin G, demonstrating its high efficiency in glycoproteomic analysis. More importantly, the generic functionalization route from amino-derived MOFs opens a new perspective in material design in sample preparation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...