Functional double-shelled silicon nanocrystals for two-photon fluorescence cell imaging: spectral evolution and tuning†
Abstract
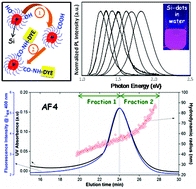
Functional near-IR (NIR) emitting nanoparticles (NPs) adapted for two-photon excitation fluorescence cell imaging were obtained starting from octadecyl-terminated silicon nanocrystals (ncSi-OD) of narrow photoluminescence (PL) spectra having no long emission tails, continuously tunable over the 700–1000 nm window, PL quantum yields exceeding 30%, and PL lifetimes of 300 μs or longer. These NPs, consisting of a Pluronic F127 shell and a core made up of assembled ncSi-OD kept apart by an octadecyl (OD) layer, were readily internalized into the cytosol, but not the nucleus, of NIH3T3 cells and were non-toxic. Asymmetrical field-flow fractionation (AF4) analysis was carried out to determine the size of the NPs in water. HiLyte Fluor 750 amine was linked via an amide link to NPs prepared with Pluronic-F127-COOH, as a first demonstration of functional NIR-emitting water dispersible ncSi-based nanoparticles.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...