A tactile sensor using a conductive graphene-sponge composite†
Abstract
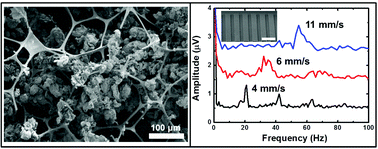
For sensors that emulate human tactile perception, we suggest a simple method for fabricating a highly sensitive force sensor using a conductive polyurethane sponge where graphene flakes are self-assembled into the porous structure of the sponge. The complete sensor device shows a sensitive and reliable detection response for a broad range of pressure and dynamic pressure that correspond to human tactile perception. Sensitivity of the sensor to detect vibration is also confirmed with vertical actuations due to slipping over micro-scale ridge structures attached on the sensors. Based on the sensor's ability to detect both pressure and vibration, the sensor can be utilized as a flexible tactile sensor.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...