Visible light response, electrical transport, and amorphization in compressed organolead iodine perovskites†
Abstract
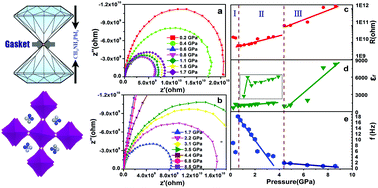
Recent scientific advances on organic–inorganic hybrid perovskites are mainly focused on the improvement of power conversion efficiency. So far, how compression tunes their electronic and structural properties remains less understood. By combining in situ photocurrent, impedance spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction (XRD) measurements, we have studied the electrical transport and structural properties of compressed CH3NH3PbI3 (MAPbI3) nanorods. The visible light response of MAPbI3 remains robust below 3 GPa while it is suppressed when it becomes amorphous. Pressure-induced electrical transport properties of MAPbI3 including resistance, relaxation frequency, and relative permittivity have been investigated under pressure up to 8.5 GPa by in situ impedance spectroscopy measurements. These results indicate that the discontinuous changes of these physical parameters occur around the structural phase transition pressure. The XRD studies of MAPbI3 under high pressure up to 20.9 GPa show that a phase transformation below 0.7 GPa, could be attributed to the tilting and distortion of PbI6 octahedra. And pressure-induced amorphization is reversible at a low density amorphous state but irreversible at a relatively higher density state. Furthermore, the MAPbI3 nanorods crush into nanopieces around 0.9 GPa which helps us to explain why the mixed phase of tetragonal and orthorhombic was observed at 0.5 GPa. The pressure modulated changes of electrical transport and visible light response properties open up a new approach for exploring CH3NH3PbI3-based photo-electronic applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...