Dibenzofurans and derivatives from lichens and ascomycetes†
Abstract
Covering: up to 2016.
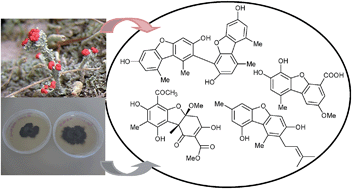
When looking for dibenzofuran in the biochemical databases, most papers and reviews deal with pollutants and polychlorinated dibenzofurans like dioxins. But dibenzofurans are also biosynthetized by a wide diversity of organisms in nature. Even if dibenzofurans from natural sources represent a small class of secondary metabolites, compared to flavonoids, xanthones or terpenoids, they are often endowed with interesting biological properties which have been recently described. This review provides an update on papers describing dibenzofurans from lichens, ascomycetes and cultured mycobionts. Other sources, such as basidiomycetes, myxomycetes or plants produce sporadically interesting dibenzofurans in terms of structures and activities.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...