How does the chain length of PEG functionalized at the outer surface of mesoporous silica nanoparticles alter the uptake of molecules?
Abstract
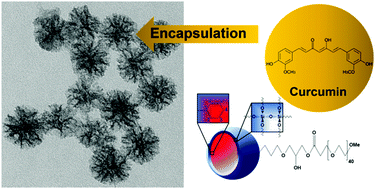
The current work describes the development of new mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) containing a high content of phenyl groups (hydrophobic species) inside the mesopores and externally functionalized with polyethylene glycol (PEG), a hydrophilic moiety, to provide biocompatibility and colloidal stability. The MSNs were encapsulated with curcumin, a versatile hydrophobic drug for biological use. The ability of silica nanoparticles to optimize the solubility of this biologically-active molecule in water was investigated. Nanoparticles were characterized using 13C and 29Si Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR), thermal analysis (TGA and DTA), nitrogen sorption analysis, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), dynamic light scattering (DLS) and zeta potential (PZ). We assessed the curcumin water solubility using the pegylated nanoparticles as well as the influence of the PEG chain length (500 and 2000 Da) and its concentration on the encapsulation process. The results indicate that the higher the PEG chain length the lower the MSN encapsulation capacity for curcumin, possibly due to steric factors. However, all of the nanoparticles largely improved curcumin solubility in water.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...