Fabrication of a label-free electrochemical immunosensor using a redox active ferrocenyl dendrimer
Abstract
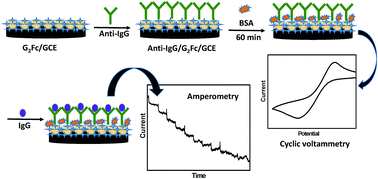
We report an IgG (=immunoglobulin) electrochemical immunosensor using a newly synthesized redox-active ferrocenyl dendrimer of generation 2 (G2Fc) as a voltammetric transducer. The ferrocenyl dendrimer N(CH2CH2C(O)NHCH2CH2NHC(O)Fe(η5-C5H4)(η5-C5H5))(CH2CH2N(CH2CH2C(O)NHCH2CH2NHC(O)Fe(η5-C5H4)(η5-C5H5))2)2 (G2Fc) was used as a functional moiety to immobilize the antibody on the surface of the electrode. A sandwich immunosensor of the type IgG/Bovine serum albumin (BSA)/anti-IgG/G2Fc/glassy carbon electrode (GCE) was fabricated. The electrochemical properties of G2Fc were thoroughly studied in aqueous and non-aqueous electrolytes with varying scan rates. The incubation time was optimized for better analytical performance of the immunosensor. It is found that the developed amperometric immunosensor is sensitive to a concentration of IgG as low as 2 ng mL−1.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...