Spontaneous 2′-deoxyguanosine alkylation by a new generation of topoisomerase I inhibitors of the camptothecin family†
Abstract
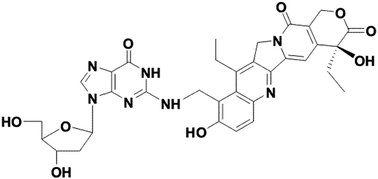
We present NMR and LC-MS evidence that 7-ethyl-9-(N-morpholinyl)methyl-10-hydroxycamptothecin spontaneously binds covalently to 2′-deoxyguanosine under near-physiological conditions. The 2-NH2 is alkylated selectively independent of conditions, either in pure water at pH 6 or in 25 mM NaCl/25 mM potassium phosphate at pH 7. This is the first documented case of the spontaneous covalent binding of 2′-deoxyguanosine by a potential topoisomerase I inhibitor. This type of camptothecin derivative (a 9-alkylaminomethyl-substituted derivative of the parent SN38, 7-ethyl-10-hydroxycamptothecin) may potentially be active in vivo because it belongs to the class of camptothecin derivatives (including Camptosar or Hycamtin) used clinically as chemotherapeutic agents for the treatment of cervical, colon, and breast cancer.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...