Efficient solid phase extraction of codeine from human urine samples using a novel magnetic molecularly imprinted nanoadsorbent and its spectrofluorometric determination
Abstract
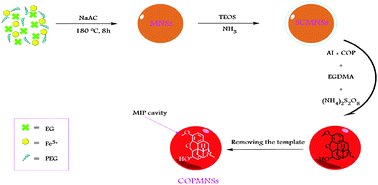
From a medical or clinical point of view, to assess toxicity, adverse effects, interactions and therapeutic efficiency, monitoring drug levels in body fluids, such as urine and plasma, has become increasingly necessary. This study reports on a novel method for determination of trace concentration levels of codeine phosphate in human urine samples. In this regard, a solid phase extraction step, based on a novel magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer nanoadsorbent, has been developed to be used prior to spectrofluorometric analysis of the drug. After optimization of various factors, such as pH, contact time, adsorbent dosage and desorbing solvent, the results showed that using the proposed method sensitive and accurate determination of the drug in the concentration range of 2.0–500.0 ng mL−1 with the detection limit of 0.67 ng mL−1 is achievable. The urine sample analysis results show that a powerful method for codeine phosphate determination has been proposed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...