Influence of the amino acid side chain on peptide bond hydrolysis catalyzed by a dimeric Zr(iv)-substituted Keggin type polyoxometalate†
Abstract
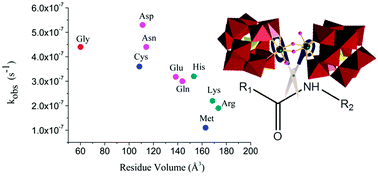
Peptide bond hydrolysis of 18 different dipeptides, divided into four groups depending on the nature of the amino acid side chain, by the dimeric Zr(IV)-substituted Keggin type polyoxometalate (POM) (Et2NH2)8[{α-PW11O39Zr-(μ-OH)(H2O)}2]·7H2O (1) was studied by means of kinetic experiments and 1H/13C NMR spectroscopy. The observed rate constants highly depend on the bulkiness and chemical nature of the X amino acid side chain. X-Ser and X-Thr dipeptides showed increased reactivity due to intramolecular nucleophilic attack of the hydroxyl group in the side chain on the amide carbon, resulting in a reactive ester intermediate. A similar effect in which the amino acid side chain acted as an internal nucleophile was observed for the hydrolysis of Gly-Asp. Interestingly, in the presence of 1 deamidation of Gly-Asn and Gly-Gln into Gly-Asp and Gly-Glu was observed. Dipeptides containing positively charged amino acid side chains were hydrolyzed at higher rates due to electrostatic interactions between the negatively charged POM surface and positive amino acid side chains.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Emergent Polyoxometalates and Soft-oxometalates

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...