Synthesis and biological evaluation of benzocyclooctene-based and indene-based anticancer agents that function as inhibitors of tubulin polymerization†‡
Abstract
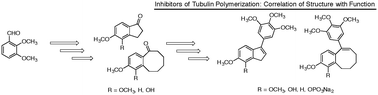
The natural products colchicine and combretastatin A-4 (CA4) have been inspirational for the design and synthesis of structurally related analogues and spin-off compounds as inhibitors of tubulin polymerization. The discovery that a water-soluble phosphate prodrug salt of CA4 (referred to as CA4P) is capable of imparting profound and selective damage to tumor-associated blood vessels paved the way for the development of a new therapeutic approach for cancer treatment utilizing small-molecule inhibitors of tubulin polymerization that also act as vascular disrupting agents (VDAs). Combination of salient structural features associated with colchicine and CA4 led to the design and synthesis of a variety of fused aryl-cycloalkyl and aryl-heterocyclic compounds that function as inhibitors of tubulin polymerization. Prominent among these compounds is a benzosuberene analogue (referred to as KGP18), which demonstrates sub-nM cytotoxicity against human cancer cell lines and functions (when administered as a water-soluble prodrug salt) as a VDA in mouse models. Structure activity relationship considerations led to the evaluation of benzocyclooctyl [6,8 fused] and indene [6,5 fused] ring systems. Four benzocyclooctene and four indene analogues were prepared and evaluated biologically. Three of the benzocyclooctene analogues were active as inhibitors of tubulin polymerization (IC50 < 5 μM), and benzocyclooctene phenol 23 was comparable to KGP18 in terms of potency. The analogous indene-based compound 31 also functioned as an inhibitor of tubulin polymerization (IC50 = 11 μM) with reduced potency. The most potent inhibitor of tubulin polymerization from this group was benzocyclooctene analogue 23, and it was converted to its water-soluble prodrug salt 24 to assess its potential as a VDA. Preliminary in vivo studies, which utilized the MCF7-luc-GFP-mCherry breast tumor in a SCID mouse model, demonstrated that treatment with 24 (120 mg kg−1) resulted in significant vascular shutdown, as evidenced by bioluminescence imaging at 4 h post administration, and that the effect continued at both 24 and 48 h. Contemporaneous studies with CA4P, a clinically relevant VDA, were carried out as a positive control.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...