Design, synthesis and P-gp induction activity of aryl phosphonate esters: identification of tetraethyl-2-phenylethene-1,1-diyldiphosphonate as an orally bioavailable P-gp inducer†‡
Abstract
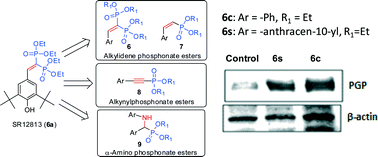
The clearance of amyloid-beta is mediated by the P-glycoprotein (P-gp) transporter pump located at the blood brain barrier. Therefore, the induction of P-gp has been considered as a potential therapeutic strategy for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. The expression of P-gp is regulated through a nuclear receptor, pregnane X receptor (PXR). Thus, herein we investigated the potential of a known PXR activator, diphosphonate ester SR12813 (6a), for P-gp induction activity and further studied its structure–activity relationship. The diphosphonate ester SR12813 along with three series of analogs, viz. aryl alkylidene, aryl alkynyl, and aryl α-amino phosphonate esters, were synthesized and screened for P-gp induction activity in P-gp overexpressing adenocarcinoma LS180 cells using rhodamine 123 efflux assay. The parent compound SR12813 along with several new analogs displayed P-gp induction activity at 5 μM. Western blot analysis indicated that tetraethyl-2-phenylethene-1,1-diyldiphosphonate (6c) and tetraethyl-2-(anthracene-10-yl)ethene-1,1-diyldiphosphonate (6s) showed 7–8-fold increase in P-gp expression in LS180 cells. The diphosphonate ester 6c displayed excellent aqueous solubility, no cytochrome P450 inhibition liability and no efflux pump substrate liability. Furthermore, it exhibits an excellent oral pharmacokinetic profile in BALB/c mice with AUC0–∞ of 2067 ng h mL−1 and 37.6% oral bioavailability. The results presented here clearly indicate the potential of this scaffold to increase the clearance of brain Aβ across the BBB and thus its promise for development as a potential anti-Alzheimer agent.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...