Design, synthesis and biological activity evaluation of novel conjugated sialic acid and pentacyclic triterpene derivatives as anti-influenza entry inhibitors†‡
Abstract
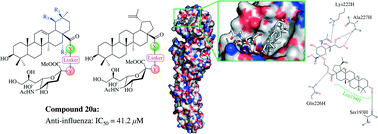
Influenza virus is a major human pathogen that causes annual epidemics and occasional pandemics. Recently, plant-derived pentacyclic triterpenes have been shown to act as highly potent anti-viral agents by efficiently preventing the attachment of the virion to the host cells. In this report, we conjugated sialic acid with oleanolic acid (OA), a natural product with broad antiviral entry activity, as well as three other analogs echinocystic acid (EA), ursolic acid (UA) and betulinic acid (BA). A total of 24 conjugated sialic acid and pentacyclic triterpene derivatives with different linkers were synthesized and evaluated for antiviral activity against influenza A/WSN/33 (H1N1) virus in MDCK cell culture. The most potent compound had an IC50 of 41.2 μM. Time-of-addition, hemagglutination inhibition (HI), surface plasmon resonance (SPR) and molecular docking assays demonstrated that compound 20a acted as an influenza virus entry inhibitor by preventing the binding of influenza virus hemagglutinin (HA) protein to host cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...