Synthesis and biodistribution of novel 99mTcN complexes of glucose dithiocarbamate as potential probes for tumor imaging†‡
Abstract
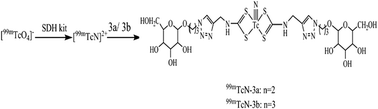
In this study, two novel glucose dithiocarbamates (3a and 3b) were successfully synthesized via a “click chemistry” route and then radiolabeled with a [99mTc![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) N]2+ core to prepare the corresponding 99mTcN complexes in high yields. Both of them were hydrophilic and had good in vitro stability. The in vivo biodistribution studies in mice bearing S180 tumor showed that the complexes accumulated in the tumor with high uptake and good retention. Through comparison, 99mTcN-3b had the advantages of higher tumor uptake, tumor/blood and tumor/muscle ratios at 2 h post-injection. The single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) image studies of 99mTcN-3b showed obvious radioactive uptake in the tumor region and the tumor-to-non-target ratio was high, suggesting that it could be regarded as a promising tumor imaging agent.
N]2+ core to prepare the corresponding 99mTcN complexes in high yields. Both of them were hydrophilic and had good in vitro stability. The in vivo biodistribution studies in mice bearing S180 tumor showed that the complexes accumulated in the tumor with high uptake and good retention. Through comparison, 99mTcN-3b had the advantages of higher tumor uptake, tumor/blood and tumor/muscle ratios at 2 h post-injection. The single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) image studies of 99mTcN-3b showed obvious radioactive uptake in the tumor region and the tumor-to-non-target ratio was high, suggesting that it could be regarded as a promising tumor imaging agent.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...