Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of indazole–pyrimidine based derivatives as anticancer agents with anti-angiogenic and antiproliferative activities†
Abstract
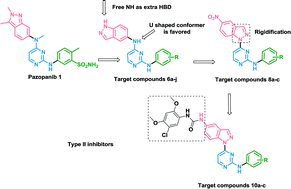
Three series of novel indazole–pyrimidine based compounds were designed, synthesized and biologically evaluated as VEGFR-2 kinase inhibitors. The most active compound 6i (IC50 = 24.5 nM) was further evaluated against a HUVEC cell line showing an IC50 of 1.37 μM. Moreover, it showed an indirect anti-angiogenic effect through the suppression of secretion of VEGF and TGF-b1 from prostate cancer cells. Five compounds were selected by the NCI for evaluation of their in vitro anticancer activity against the full NCI panel of cell lines at 10 μM. Compounds 6e and 6f were further selected for 5-dose testing. Compound 6e exerted nanomolar GI50 values against several cell lines: CCRF-CEM (901 nM), MOLT-4 (525 nM) and CAKI-1 (992 nM) and one digit micromolar activity against the rest of the cell lines ranging from 1.05 μM to 2.41 μM. Compound 6f showed one digit micromolar activity against the whole panel of cell lines ranging from 1.55 μM to 7.4 μM. A molecular docking study was employed to investigate the predicted binding mode of the target compounds with VEGFR-2, using Autodock software. Furthermore, MD simulation was implemented for compounds 6i and 10c for further validation and rationalization of their binding mode.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...