Abstract
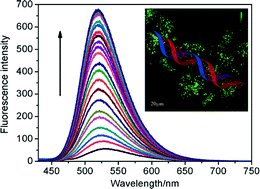
A series of novel N,N-bis(3-aminopropyl)methylamine-bridged bis-naphthalimide derivatives NI1–6 were designed and synthesized. Their cytotoxic activities against Hela, MCF-7, SGC-7901 and A549 cells were investigated. Compounds NI1–6 exhibited selectively cytotoxic activities in the tested cell lines and lower cytotoxic activities against MCF-7 cells were found except for compound NI1. NI1, the N-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazine-modified naphthalimide, showed potent cytotoxic activity in the tested cell lines with IC50 values of 2.31, 2.94, 0.88 and 1.21 μM, respectively, better than the control drug (amonafide). Furthermore, its DNA binding properties, fluorescence imaging and collective apoptosis were investigated. Interestingly, NI1 as a DNA intercalator showed fluorescence enhancement upon binding with Ct-DNA and exhibited different impacts on the cell cycle compared with amonafide. Moreover, compound NI1 showed no significant hematoxicity and cardiotoxicity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...