Synergistic activity of a short lipidated antimicrobial peptide (lipoAMP) and colistin or tobramycin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa from cystic fibrosis patients†‡
Abstract
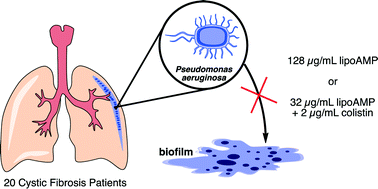
Declining pulmonary function, ultimately culminating in respiratory failure, is mainly caused by chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) infections in patients with cystic fibrosis (CF). Due to its hypermutability, allowing rapid adaptation to the selective constraints in a lung with CF, and the ability to form biofilms, P. aeruginosa is able to colonize and damage the lung by chronic infection. Exacerbations are being treated with a combination of common anti-pseudomonal antibiotics, but (pan)resistance is increasingly reported. Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) have a broad spectrum of antibacterial activity, and their effectiveness is, still, less affected by induction of resistance. Here, we explore the in vitro applicability of a RWRWRWK(C10) synthetic lipoAMP (named BA250-C10), a lipidated peptide with a C10-lipid chain attached to the C-terminus, as a novel antibacterial agent against P. aeruginosa; and in particular, its ability to inhibit biofilm formation. BA250-C10 was tested for its in vitro antibacterial activity against 20 clinical P. aeruginosa isolates from CF patients, each having a different resistance profile and ability to form biofilms. The modest antibacterial activity of the peptide against most P. aeruginosa strains (16–256 μg mL−1) was significantly increased in the presence of colistin or tobramycin, supported by the results from the checkerboard assay and growth curves. In three biofilm-forming strains, a synergistic effect was observed for BA250-C10 with colistin, but less with tobramycin. This indicates that combinations of lipidated AMPs and colistin may be further pursued as a potential novel treatment strategy against P. aeruginosa infections in CF patients.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...