Identification of a lncRNA involved functional module for esophageal cancer subtypes†
Abstract
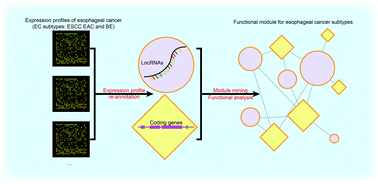
Esophageal cancer (EC) is the sixth most common cause of death from cancer and has two principal histological subtypes: esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) and esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC). In addition, Barrett's esophagus (BE), due to its strong association with EAC, is generally considered to be a premalignant condition of EAC. lncRNAs are believed to function in initiation and progression of multiple cancers, and therefore should play prominent, but unknown roles in the determination and behavior of different EC subtypes. In this study, by using expression profile re-annotation and differential expression (DE) analysis, we identified DE-lncRNAs and DE-protein-coding genes (DE-PCGs), and then constructed a lncRNA–PCG network, using co-expressed DE-lncRNAs (550) and DE-PCGs (5236), which was also annotated for EC subtypes. After module mining of the network, we obtained twenty candidate lncRNA–PCG modules that were ranked by gene expression and subtype-specification. Within the top four modules, we identified an ESCC specific module, two EAC-BE-specific modules and a heterologous module. Novel candidate lncRNAs were identified, in addition to lncRNAs known to be functionally connected to EC, and could be responsible for the subtype disparities in the GO biological process and at pathway levels.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...