Autophagy-related intrinsically disordered proteins in intra-nuclear compartments†
Abstract
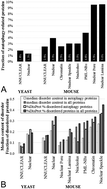
Recent analyses indicated that autophagy can be regulated via some nuclear transcriptional networks and many important players in the autophagy and other forms of programmed cell death are known to be intrinsically disordered. To this end, we analyzed similarities and differences in the intrinsic disorder distribution of nuclear and non-nuclear proteins related to autophagy. We also looked at the peculiarities of the distribution of the intrinsically disordered autophagy-related proteins in various intra-nuclear organelles, such as the nucleolus, chromatin, Cajal bodies, nuclear speckles, promyelocytic leukemia (PML) nuclear bodies, nuclear lamina, nuclear pores, and perinucleolar compartment. This analysis revealed that the autophagy-related proteins constitute about 2.5% of the non-nuclear proteins and 3.3% of the nuclear proteins, which corresponds to a substantial enrichment by about 32% in the nucleus. Curiously, although, in general, the autophagy-related proteins share similar characteristics of disorder with a generic set of all non-nuclear proteins, chromatin and nuclear speckles are enriched in the intrinsically disordered autophagy proteins (29 and 37% of these proteins are disordered, respectively) and have high disorder content at 0.24 and 0.27, respectively. Therefore, our data suggest that some of the nuclear disordered proteins may play important roles in autophagy.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...