Genome-wide targets identification of “core” pluripotency transcription factors with integrated features in human embryonic stem cells†
Abstract
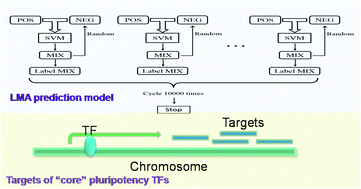
Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) play an important role in developmental biology which is still lacking clear molecular mechanisms. The “core” transcription factors (TFs) including OCT4, SOX2 and NANOG are essential for maintaining the stemness of ESCs. But the downstream targets of these “core” TFs are still ambiguous. Based on support vector machine (SVM) technology, this study develops a label method algorithm (LMA) for genome-wide target identification of “core” TFs in humans, which eliminates the need for negative training samples. This method integrates histone modifications and TF binding motifs as identification features. Compared with a previous mapping-convergence (M-C) algorithm, the LMA can provide more stable and reliable predictions. 4796, 3166 and 4384 target genes of OCT4, SOX2 and NANOG, respectively, were identified with the LMA model. Then verifications of the predicted targets were carried out based on their functional consistency and their connection degree in networks from a computational system biology perspective. The results showed that the targets of “core” TFs present higher gene functional similarity and closer connection distance than background levels.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...