Drop formation using ferrofluids driven magnetically in a step emulsification device†
Abstract
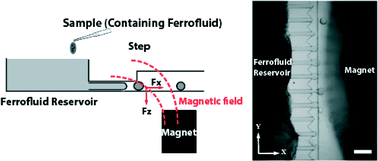
We present a microfluidic droplet generation technique, where instead of pumps, only magnetic field gradient strength adjusted by the position of an external magnet is used for controllable emulsification of ferrofluid containing solutions. Uniform droplet generation at frequencies O(1–100) Hz per channel for long periods of time (10s of minutes) were easily achieved. In this method, adding magnetic nanoparticles (10 nm) into aqueous solutions imparts a magnetic body force on the fluid in the presence of an external magnetic field gradient. Consequently, the aqueous fluid moves toward the position of an external magnet and towards a junction with a larger width and height oil filled reservoir. Emulsification occurs at the junction due to a rapid change in surface tension forces due to the abrupt change in channel height. Droplet generation rate could be controlled by adjusting surface tension/viscosity, number of channels, and strength of the magnetic force. The geometry of the channel, rather than flow rates or magnetic force, plays the dominant role in defining the droplet size. In addition, reagents mixed with ferrofluids could also be introduced from two or more separate inlets and mixed prior to emulsification as they move toward the step driven by magnetic force. Mixing reagents on chip and forming droplets all within a small foot-print defined by movement of an external magnet is a unique feature of this method suitable for point-of-care diagnostics and other bioengineering applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...