A portable smart phone-based plasmonic nanosensor readout platform that measures transmitted light intensities of nanosubstrates using an ambient light sensor†
Abstract
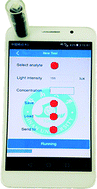
Plasmonic nanosensors may be used as tools for diagnostic testing in the field of medicine. However, quantification of plasmonic nanosensors often requires complex and bulky readout instruments. Here, we report the development of a portable smart phone-based plasmonic nanosensor readout platform (PNRP) for accurate quantification of plasmonic nanosensors. This device operates by transmitting excitation light from a LED through a nanosubstrate and measuring the intensity of the transmitted light using the ambient light sensor of a smart phone. The device is a cylinder with a diameter of 14 mm, a length of 38 mm, and a gross weight of 3.5 g. We demonstrated the utility of this smart phone-based PNRP by measuring two well-established plasmonic nanosensors with this system. In the first experiment, the device measured the morphology changes of triangular silver nanoprisms (AgNPRs) in an immunoassay for the detection of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA). In the second experiment, the device measured the aggregation of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) in an aptamer-based assay for the detection of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The results from the smart phone-based PNRP were consistent with those from commercial spectrophotometers, demonstrating that the smart phone-based PNRP enables accurate quantification of plasmonic nanosensors.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...