Real-time imaging and quantitative analysis of doxorubicin transport in a perfusable microvessel platform†
Abstract
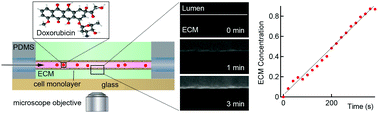
Here we report on real-time imaging and quantitative analysis of solute transport in perfusable cylindrical microvessels formed from Madin–Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells embedded in a collagen matrix. Fluorescence microscopy was used to image the kinetics of doxorubicin transport following injection. To assess the role of efflux pumps on transport, experiments were performed in microvessels formed from MDCK.2, MDCKII-w/t, and MDCKII-MDR1 cells. MDCKII-w/t and MDCKII-MDR1 showed significant doxorubicin accumulation in the cells, characteristic of the pharmacokinetics of doxorubicin. We present a model for doxorubicin transport that takes into account transport across the cell layer. These results demonstrate how real-time imaging of cell microvessels can be used to analyze the mechanisms of transport and distribution following systemic delivery.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...