The strong association of condensed phenolic moieties in isolated lignins with their inhibition of enzymatic hydrolysis†
Abstract
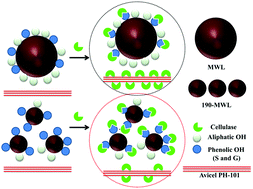
Residual lignin plays an inhibitory role in the enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulosic biomass. In this study, we examined the structural changes in isolated lignins from the hot water hydrothermal pretreatment of aspen and their inhibitory effects on the enzymatic hydrolysis of Avicel. The functional groups of the isolated lignins were determined using quantitative 13C, 2D HSQC and 31P NMR. The increase in pretreatment severity significantly increased the condensed and non-condensed syringyl and guaiacyl OH group content in the isolated lignins, but decreased the aliphatic OH, p-hydroxybenzoate OH and carboxylic OH group content. A compelling adverse association (r2 = 0.998) was observed between the condensed syringyl and guaiacyl phenolic OH group content in lignins and their inhibitory effects on enzymatic hydrolysis. Langmuir adsorption isotherms showed that a higher pretreatment severity resulted in a higher binding ability between the isolated lignins and the cellulase enzymes, which led to more non-productive binding. It is hypothesized that condensed syringyl and guaiacyl phenolic units are mainly responsible for the inhibitory effect of lignin on enzymatic hydrolysis, in which the condensed aromatic rings enhance the hydrophobic interactions and the phenolic OH group boosts the hydrogen bonding. The combination of hydrophobic interactions and hydrogen bonding can further intensify undesirable non-productive binding.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...