Selective aldol condensation of biomass-derived levulinic acid and furfural in aqueous-phase over MgO and ZnO†
Abstract
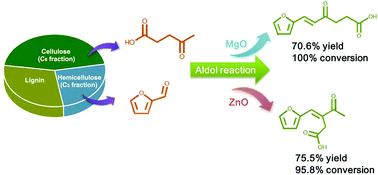
The aldol condensation of furfural with levulinic acid in the aqueous phase was investigated over a series of solid catalysts, including oxides (MgO, ZnO, TiO2, ZrO2, MgO–Al2O3, CeO2, Nb2O5, SnO2, and WO3) and acidic zeolites (HY, Hβ, HZSM-5, H-MOR, and SAPO-34). Two isomeric condensation products, β- and δ-furfurylidenelevulinic acids (β- and δ-FDLA), were produced after acidification. MgO and ZnO were evaluated as active and selective catalysts with respect to aqueous phase aldol condensation. MgO gave a high selectivity towards δ-FDLA due to the water-tolerant basicity. In contrast, ZnO was highly selective towards β-FDLA, indicative of an acid-catalyzed aldol reaction mechanism. Nano-ZnO with a relatively high surface area gave rise to enhanced yields of β-FDLA. In-depth investigations revealed that the exposed surface hydroxyl groups on ZnO worked as active sites for the aldol reaction.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...