First evidence of metal transfer into hydrophobic deep eutectic and low-transition-temperature mixtures: indium extraction from hydrochloric and oxalic acids†
Abstract
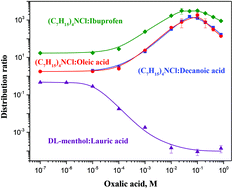
This is the first report on metallic species transfer from aqueous solutions into hydrophobic deep eutectic and low-transition-temperature mixtures. The near-critical and strategic metal, indium, has been successfully extracted from hydrochloric and oxalic acid media into quaternary ammonium- and menthol-based mixtures containing carboxylic acids.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...