Highly efficient I2 capture by simple and low-cost deep eutectic solvents†
Abstract
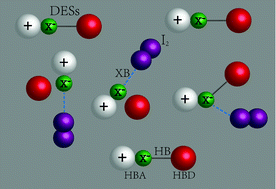
The efficient removal and storage of radioactive nuclear contaminants including an isotope of iodine (131I) has attracted great concern especially after the explosion of the Fukushima nuclear power plant. In this study, deep eutectic solvents (DESs) are proposed for the removal and storage of iodine (I2). These DESs can be obtained by simply mixing two simple components (also cheap and biodegradable), which form liquids with melting points far below that of the individual components. A series of hydrogen bond donors (HBDs) and hydrogen bond acceptors (HBAs) are selected for the preparation of DESs. The properties and I2 capture efficiency of the prepared DESs have been investigated. The results indicate that some DESs have higher efficiencies for I2 removal than the previously reported materials. Among them, ChI–methylurea shows the best I2 uptake efficiency of approximately 100% within 5 hours. Moreover, ChI–methylurea exhibits a good capability of I2 storage with only 4.6% of the iodine evaporated after 10 hours of strong N2 sweeping, which is also important since I2 is easy to sublimate. Additional calculations also suggest that the high efficiency for I2 capture by DESs mainly comes from the formation of halogen bonding (XB) between DESs and I2. This work opens a new way for the application of DESs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...