Ru–B nanoparticles on metal–organic frameworks as excellent catalysts for hydrogenation of benzene to cyclohexane under mild reaction conditions†
Abstract
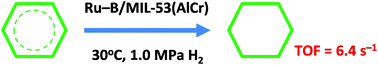
The ever-increasing industrial demands for nylon-6 and nylon-66 and the more and more stringent regulations on particulate emission in exhaust gases necessitate the development of an energy-efficient and environment-friendly method for saturation hydrogenation of benzene and its derivatives. However, the hydrogenation of benzene is usually conducted at a high temperature and/or under high H2 pressure, which is energy-consuming and of low environmental safety. Here, we prepared amorphous Ru–B/MIL-53(Al, Cr, and AlCr) catalysts via the wetness impregnation–chemical reduction method, which were comprehensively characterized by a combination of techniques. We found that the Ru–B/MIL-53 catalysts could catalyse the hydrogenation of benzene to cyclohexane under mild reaction conditions of 30 °C and 1.0 MPa of H2 with high efficiency, among which the Ru–B/MIL-53(AlCr) catalyst exhibited the highest turnover frequency (TOF) in terms of benzene of 6.4 s−1. Moreover, this catalyst showed good recyclability and high activities in the hydrogenation of toluene, o-xylene, m-xylene, p-xylene, and mesitylene as well, which shows promise for the application of the Ru–B/MIL-53 catalysts in the industrially important and environmentally desirable hydrogenation reaction of benzene and its derivatives.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...