A bilateral electrochemical hydrogen pump reactor for 2-propanol dehydrogenation and phenol hydrogenation
Abstract
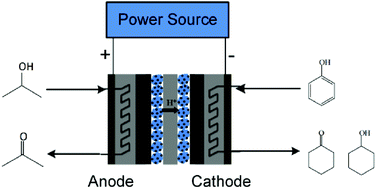
A bilateral electrochemical hydrogen pump reactor is proposed for the first time. In one electrochemical hydrogen pump (EHP) configuration, in situ adsorbed hydrogen atoms for phenol hydrogenation at the cathode are donated by the dehydrogenation of 2-propanol instead of a conventional H2 or H2O anode feedstock. For the anodic 2-propanol dehydrogenation EHP reactor, by increasing Pt–Ru/C catalyst loading and applying a pulse current operation, the applied potential can be controlled below 0.2 V, which is much lower than the thermodynamic dissociation potential of water (1.23 V). For the cathodic cyclohexanone hydrogenation EHP reactor, the hydrogenation rate reaches 73.9 mmol h−1 g−1Pd, nearly three times of that in aqueous-phase selective hydrogenation reactors. Pd/C and Pt/C catalysts have high catalytic selectivity to cyclohexanone (95.5%) and cyclohexanol (95.4%), respectively. In the bilateral EHP reactor, 2-propanol dehydrogenation and phenol hydrogenation are completed simultaneously, exhibiting a comparable hydrogenation rate, selectivity and conversion to that in the individual EHP reactors. The feasibility of the bilateral EHP reactor provides a novel idea to efficiently integrate multiple reactors into one configuration, which greatly simplifies hydrogen production, storage and transportation, as well as reactor equipment.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...