Antidiabetic (type 2) effects of Lactobacillus G15 and Q14 in rats through regulation of intestinal permeability and microbiota†
Abstract
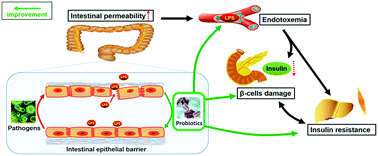
The antidiabetic effects of Lactobacillus. paracasei subsp. paracasei G15 and Lactobacillus. casei Q14 in high fat diet and streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic (T2D) rats were evaluated in this study. The strains were separated from Chinese traditional fermented dairy food. Administration of G15 and Q14 for 6 weeks significantly improved the glucose tolerance and reduced the HbA1c levels in T2D rats. The probiotic treatment reduced the intestinal mucosal permeability and improved the epithelial barrier function through modification of the gut microbiota, which in turn lowered circulating LPS and inflammation cytokines, including IL-1β and IL-8, and eventually alleviated the inflammatory status and islet β-cell dysfunction. Combination of Q14 and metformin reversed the thymic atrophy and both G15 and Q14 lowered the circulating IL-6 level, indicating the immune-modulating potential of the strains. Lactobacillus. paracasei subsp. paracasei G15 and Lactobacillus. casei Q14 provide an insight into the biotherapy application of traditional fermented foods and their functional ingredients in the treatment of diabetes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...