Protective effects of glycyrrhizic acid from edible botanical glycyrrhiza glabra against non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in mice
Abstract
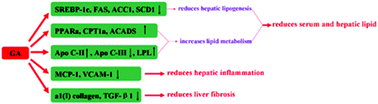
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is a syndrome with simultaneous severe hepatic steatosis, lobular inflammation and pericelluar fibrosis. The purpose of the present study is to investigate the protective effect of glycyrrhizic acid (GA), a natural triterpene glycoside from edible botanical glycyrrhiza glabra, on NASH induced by a methionine and choline-deficient (MCD) diet in mice, and further to elucidate the mechanisms of GA protection. Serum ALT and AST assay and H&E staining were used to identify the amelioration of the liver histopathological changes. Serum and hepatic lipid assay and Oil Red O staining were used to measure lipid accumulation. Hepatic inflammatory and fibrosis gene determination, as well as Mason Trichrome and Sirius Red staining were used to determine the reduction of hepatic inflammation and pericelluar fibrosis. Quantitative real-time PCR and Western blot assays were used to elucidate the mechanisms underlying GA protection. The results indicated that GA treatment reduced hepatic lipogenesis through a decrease in hepatic levels of SREBP-1c, FAS, ACC1 and SCD1, and increased lipid metabolism through an induction of PPARα, CPT1α, ACADS and LPL. GA also reduced hepatic inflammation via a decrease in the expression of the hepatic inflammatory genes MCP-1 and VCAM-1. In addition, GA reduced liver fibrosis through limiting HSC activation and collagen deposition. In conclusion, GA produces a markedly protective effect against NASH induced by a methionine and choline-deficient (MCD) diet in mice.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...