Mediterranean diet and faecal microbiota: a transversal study
Abstract
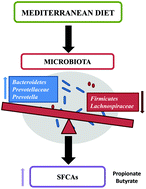
Despite the existing evidence on the impact of olive oil and red wine on the intestinal microbiota, the effect of the global Mediterranean Diet (MD) has not been sufficiently studied. We explored the association between the adherence to a Mediterranean dietary pattern, and its components, with faecal microbiota in a cohort of adults with non-declared pathology. This transversal study involved 31 adults without a previous diagnosis of cancer, autoimmune or digestive diseases. Based on the data obtained by means of an annual food frequency questionnaire (FFQ), and the information existing in the literature, a Mediterranean Diet Score (MDS) was calculated. Dietary fibre was obtained from Marlett et al. tables and Phenol-Explorer Database was used for phenolic compounds intake. Quantification of microbial groups was performed by Ion Torrent 16S rRNA gene-based analysis and quantification of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) was performed using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (MS). MDS was associated with a higher abundance of Bacteroidetes (p = 0.001), Prevotellacea (p = 0.002) and Prevotella (p = 0.003) and a lower concentration of Firmicutes (p = 0.003) and Lachnospiraceae (p = 0.045). Also, in subjects with MDS ≥ 4, higher concentrations of faecal propionate (p = 0.034) and butyrate (p = 0.018) were detected. These results confirm the complexity of the diet-microbiota interrelationship.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...