Quantitative proteomic analysis of milk fat globule membrane (MFGM) proteins in human and bovine colostrum and mature milk samples through iTRAQ labeling†
Abstract
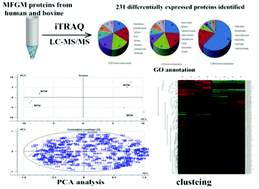
Milk fat globule membrane (MFGM) proteins have many functions. To explore the different proteomics of human and bovine MFGM, MFGM proteins were separated from human and bovine colostrum and mature milk, and analyzed by the iTRAQ proteomic approach. A total of 411 proteins were recognized and quantified. Among these, 232 kinds of differentially expressed proteins were identified. These differentially expressed proteins were analyzed based on multivariate analysis, gene ontology (GO) annotation and KEGG pathway. Biological processes involved were response to stimulus, localization, establishment of localization, and the immune system process. Cellular components engaged were the extracellular space, extracellular region parts, cell fractions, and vesicles. Molecular functions touched upon were protein binding, nucleotide binding, and enzyme inhibitor activity. The KEGG pathway analysis showed several pathways, including regulation of the actin cytoskeleton, focal adhesion, neurotrophin signaling pathway, leukocyte transendothelial migration, tight junction, complement and coagulation cascades, vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway, and adherens junction. These results enhance our understanding of different proteomes of human and bovine MFGM across different lactation phases, which could provide important information and potential directions for the infant milk powder and functional food industries.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...