Dose-related effects of ferric citrate supplementation on endoplasmic reticular stress responses and insulin signalling pathways in streptozotocin–nicotinamide-induced diabetes
Abstract
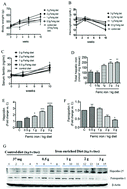
Diabetic patients are at high risk of developing anemia; however, pharmacological doses of iron supplementation may vary greatly depending on diabetes-related complications. The aim of this study was to investigate the dose-dependent effect of iron on glucose disposal with a special focus on endoplasmic reticular (ER) stress, iron metabolism, and insulin signalling pathways. Diabetes was induced in overnight fasted rats by intraperitoneal (i.p.) injections of 40 mg kg−1 streptozotocin (STZ) and 100 mg kg−1 nicotinamide. Diabetic rats were fed a standard diet (36.7 mg ferric iron per kg diet) or pharmacological doses of ferric citrate (0.5, 1, 2, and 3 g ferric iron per kg diet). Ferric citrate supplementation showed a dose-related effect on hepatic ER stress responses and total iron levels, which were associated with increased hepcidin and decreased ferroportin expressions. Iron-fed rats had increased sizes of their pancreatic islets and hyperinsulinemia compared to rats fed a standard diet. A western blot analysis revealed that iron feeding decreased total insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS1), phosphorylated IRS1ser307, and AS160 but increased phosphorylated GSK-3β. Iron supplementation inhibited the nuclear translocation of AKT but promoted FOXO1 translocation to nuclei. Ferric citrate supplementation showed a dose-related effect on ER stress responses, hepatic iron, and the insulin signaling pathway. Adverse effects were more evident at high iron doses (>1 g ferric iron per kg diet), which is equivalent to a 60 kg human male consuming >500 mg elemental iron per day.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...