Proteomic analysis of intestinal tissues from mice fed with Lentinula edodes-derived polysaccharides†
Abstract
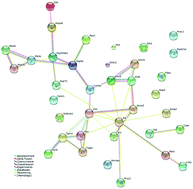
Lentinula edodes-derived polysaccharides are well known for their immunomodulation and antitumor activities. However, the mechanisms of action have not been fully elucidated. This study presents proteomic analysis of the colon and small intestine from mice fed with an immunostimulating heteropolysaccharide L2 from the fruit body of L. edodes. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2-DE) and MALDI-TOF-TOF MS/MS were employed to characterize the protein profiles. Twenty nine gel spots representing 20 proteins in colon tissues and 38 gel spots in small intestine tissues representing 23 proteins were identified as showing significant changes in abundance. These differential proteins in abundance are mainly involved in metabolism, binding, structural components, and response to stimulus. Protein–protein interaction network analysis demonstrated mapping of the 20 colon proteins to a 7-protein and a 3-protein sub-network, and mapping of the 23 small intestine proteins to a 9-protein and a 5-protein sub-network. All the 40 altered proteins were integrated into a unified network containing 25 proteins, suggesting the existence of a concerted mechanism, although acting on the colon and small intestine separately. These findings facilitate the understanding of the regulatory mechanism in response to L2 treatment.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...